
11.5 Database System Model
Database model shows the logical structure of a database, including the relationships and constraints that determine how data can be stored and accessed. A data model consists of rules and standards that define how the database organizes data. Most data models can be represented by an accompanying database diagram.
-
Relational model
-
Objected-oriented model
-
Object-relational model
-
Multidimensional model
Relational Model
The model accounts for the types of relationships between those tables, including one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships. The relational model sorts data into tables, each of which consists of columns and rows.

Object-Oriented Model
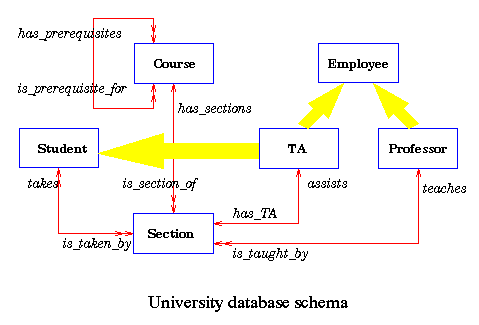
This model defines a database as a collection of objects with associated features and methods. There are 2 kinds of database which are multimedia database and hypertext database.
A multimedia database incorporates media, such as images, that could not be stored in a relational database.
A hypertext database allows any object to link to any other object. It’s useful for organizing lots of disparate data, but it’s not ideal for numerical analysis.
Object Relational Model
This hybrid database model combines the simplicity of the relational model with some of the advanced functionality of the object-oriented database model. It allows designers to incorporate objects into the familiar table structure.
The benefits provided are:
-
able to support many types of geometry
-
ease of use in creating and maintaining indexes and in performing spatial queries
-
optimal performance
-
index maintenance by the Oracle database

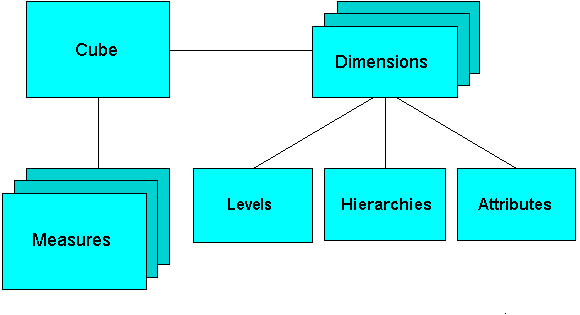
Multidimensional Model (MDDM)
MDDM was developed for implementing data warehouse and data marts. Its provide both a mechanism to store data and a way for business analysis.
Types of MDDM:
a) Data Cube Model
b) Star Scheme Model
c) Snow Flake Schema Model
d) Fact Constellations